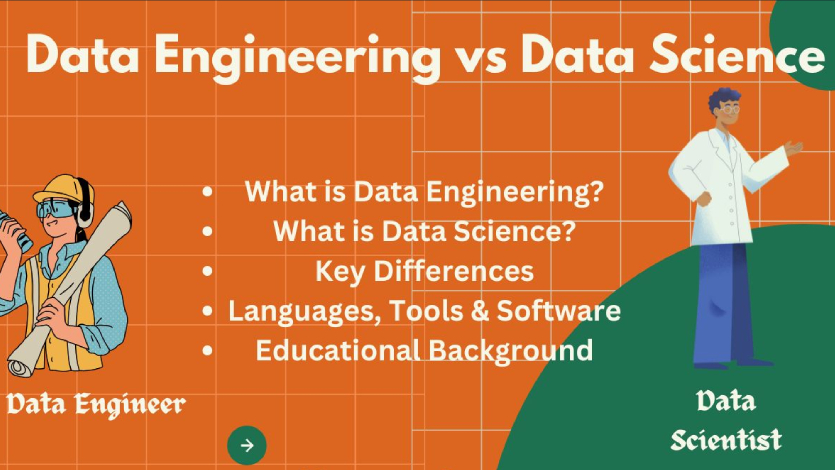
In today's data-driven world, terms like Data Engineering and Data Science often get used interchangeably. While they work closely together, they actually play very different roles in turning raw information into useful insights. To put it simply: data engineers build the systems that collect and organize data, while data scientists analyze that data to make sense of it.
Understanding the difference is important for businesses and individuals alike—especially as organizations increasingly rely on data to guide decisions. Let's break it down in clear, practical terms.
What is Data Engineering?
Think of data engineering as the foundation of a house. Before you can decorate or live in a house, you need strong walls, plumbing, and wiring. Data engineers are the ones who design and build those foundations for data.
Their job is to:
In short, data engineering is about making raw data usable. Without this step, data scientists would have nothing clean or structured to work with.
What is Data Science?
Now imagine moving into the house. You want to decorate it, choose colors, and make it comfortable. That's the role of data science—turning the structure into something meaningful and insightful.
Data scientists use the prepared data to:
If data engineers focus on the “plumbing” of data, data scientists are like “detectives” who look for answers within it.
Key Differences Between Data Engineering and Data Science
| Aspect | Data Engineering | Data Science |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Collecting, cleaning, and managing data | Analyzing and interpreting data |
| Goal | Make data accessible and reliable | Extract insights and predictions |
| Skills Needed | SQL, Python, ETL (Extract-Transform-Load), cloud systems | Statistics, machine learning, visualization, Python/R |
| Tools | Hadoop, Spark, Kafka, BigQuery, Snowflake | Pandas, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Tableau, Scikit-learn |
| Outcome | Organized data pipelines and storage systems | Reports, models, forecasts, and business insights |
How They Work Together
Even though their roles are different, data engineers and data scientists must collaborate. A data scientist cannot build accurate models without reliable, well-structured data. Similarly, a data engineer's work has little business value unless it enables analysis and insights
Here's an example:
Together, they create a complete loop—from data collection to decision-making.
Why Businesses Need Both
Many companies make the mistake of hiring only data scientists without realizing that good analysis is impossible without solid data engineering. Similarly, investing only in data engineering without analysis means the business has lots of clean data but no insights.
In 2025, successful organizations are building data teams that combine both roles. Data engineers ensure a strong data infrastructure, while data scientists unlock the real business value hidden inside.
The Bottom Line
Data Engineering and Data Science are two sides of the same coin. One focuses on building reliable data systems, while the other focuses on making sense of that data.
When both work hand in hand, businesses can make smarter decisions, create better products, and gain a real competitive advantage.